How Blockchain Works: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Technology
- The Role of Cryptography in Securing Blockchain Transactions
- Exploring the Decentralized Nature of Blockchain Networks
- Smart Contracts: Automating Transactions on the Blockchain
- The Process of Mining and Verifying Transactions on the Blockchain
- Real-World Applications of Blockchain Technology
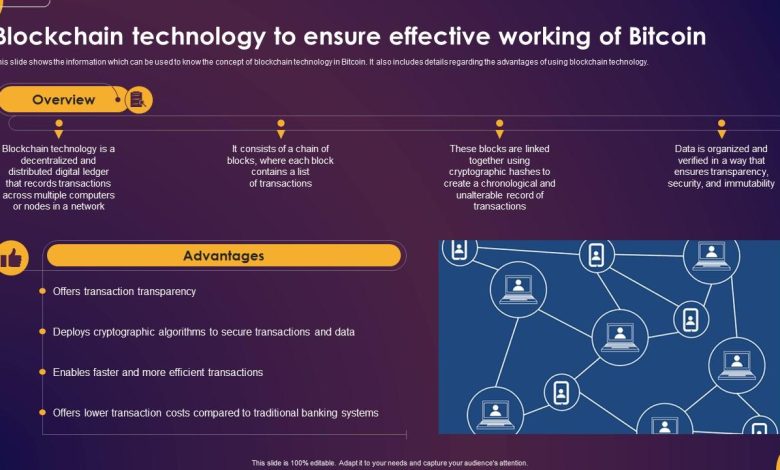
Understanding the Basics of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that securely records transactions across a network of computers. The blockchain consists of blocks of data that are linked together in a chronological order, forming a chain. Each block contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a unique cryptographic hash that connects it to the previous block.
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its transparency and immutability. Once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted without affecting all subsequent blocks. This makes blockchain a highly secure and tamper-proof system for recording transactions.
Blockchain technology is most commonly associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its applications go far beyond digital currencies. It can be used to track supply chains, verify identities, facilitate smart contracts, and much more. The potential uses of blockchain technology are vast and continue to expand as the technology evolves.
Understanding the basics of blockchain technology is essential for anyone looking to explore its potential applications. By grasping the fundamental concepts of decentralization, cryptography, and consensus mechanisms, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for how blockchain works and how it can revolutionize various industries. Whether you are a developer, entrepreneur, or simply curious about emerging technologies, blockchain has the power to transform the way we interact and transact in the digital world.
The Role of Cryptography in Securing Blockchain Transactions
Cryptography plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of blockchain transactions. By utilizing complex mathematical algorithms, cryptography helps to encrypt transaction data, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to access or alter the information. This encryption process involves the use of public and private keys, which are unique to each user and are required to validate and authorize transactions on the blockchain network.
One of the key benefits of cryptography in blockchain transactions is its ability to provide a high level of security and privacy. The use of encryption techniques ensures that sensitive information, such as transaction details and user identities, remains confidential and secure. This helps to prevent fraud, hacking, and other malicious activities that could compromise the integrity of the blockchain network.
Additionally, cryptography helps to establish trust among users by verifying the authenticity of transactions and ensuring that only authorized parties can participate in the network. This is achieved through the use of digital signatures, which are created using the sender’s private key and can be verified using their public key. By using these cryptographic techniques, blockchain transactions can be securely executed without the need for intermediaries or centralized authorities.
Overall, cryptography is an essential component of blockchain technology, providing the necessary tools to secure transactions, protect user privacy, and establish trust in the decentralized network. As blockchain continues to evolve and expand into various industries, the role of cryptography will remain critical in ensuring the integrity and security of transactions on the network.
Exploring the Decentralized Nature of Blockchain Networks
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature, which sets it apart from traditional centralized systems. In a blockchain network, data is stored and managed across a distributed network of computers, known as nodes, rather than being controlled by a single central authority. This decentralized structure offers several advantages, including increased security, transparency, and resilience.
Each node in a blockchain network maintains a copy of the entire blockchain, which is a continuously growing list of records, or blocks, linked together using cryptography. This redundancy helps to prevent a single point of failure and makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to tamper with the data. Additionally, the decentralized nature of blockchain networks means that there is no single point of control, making them resistant to censorship and manipulation.
Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain networks also enables greater transparency and trust among participants. Since all transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be viewed by anyone, it creates a high level of accountability and reduces the risk of fraud. This transparency is particularly valuable in industries such as finance, supply chain management, and healthcare, where trust and security are paramount.
Smart Contracts: Automating Transactions on the Blockchain
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts run on the blockchain, ensuring that transactions are automated and irreversible once the conditions are met. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, smart contracts reduce costs and increase efficiency in various industries.
The Process of Mining and Verifying Transactions on the Blockchain
When it comes to the process of mining and verifying transactions on the blockchain, it is essential to understand the intricate steps involved. Miners play a crucial role in this process by using powerful computers to solve complex mathematical puzzles. These puzzles are known as proof-of-work algorithms, which require significant computational power to solve. Once a miner successfully solves the puzzle, they add a new block of transactions to the blockchain.
Verifying transactions on the blockchain is equally important as mining. Once a block is added to the blockchain, it undergoes a verification process to ensure the transactions within the block are valid. This verification process is carried out by nodes on the network, which are essentially computers connected to the blockchain. Nodes check the validity of each transaction by confirming that the sender has sufficient funds and that the transaction has not been tampered with.
Overall, the process of mining and verifying transactions on the blockchain is a complex but essential part of how blockchain technology works. Without miners to add new blocks and nodes to verify transactions, the blockchain would not be able to function effectively. By understanding these processes, we can appreciate the decentralized and secure nature of blockchain technology.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has a wide range of real-world applications beyond cryptocurrencies. One of the key areas where blockchain is being utilized is in supply chain management. Companies are using blockchain to track the movement of goods from the manufacturer to the end consumer. This helps in ensuring transparency and authenticity in the supply chain process.
Another significant application of blockchain technology is in the healthcare industry. By storing patient records on a blockchain, healthcare providers can securely access and share patient information, leading to improved patient care and data security. Additionally, blockchain is being used in voting systems to enhance the security and transparency of elections.
Blockchain technology is also revolutionizing the financial sector by enabling faster and more secure cross-border transactions. Banks and financial institutions are exploring the use of blockchain for remittances and international payments. Moreover, blockchain is being used in the real estate industry to streamline property transactions and reduce fraud.
Furthermore, blockchain technology is finding applications in the legal sector for smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of disputes. Additionally, blockchain is being explored in the energy sector for peer-to-peer energy trading and grid management.
In conclusion, blockchain technology has the potential to transform various industries by enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency. As more organizations adopt blockchain solutions, we can expect to see further innovations and advancements in different sectors.






